- Periodic Table Nitrogen Mass Number
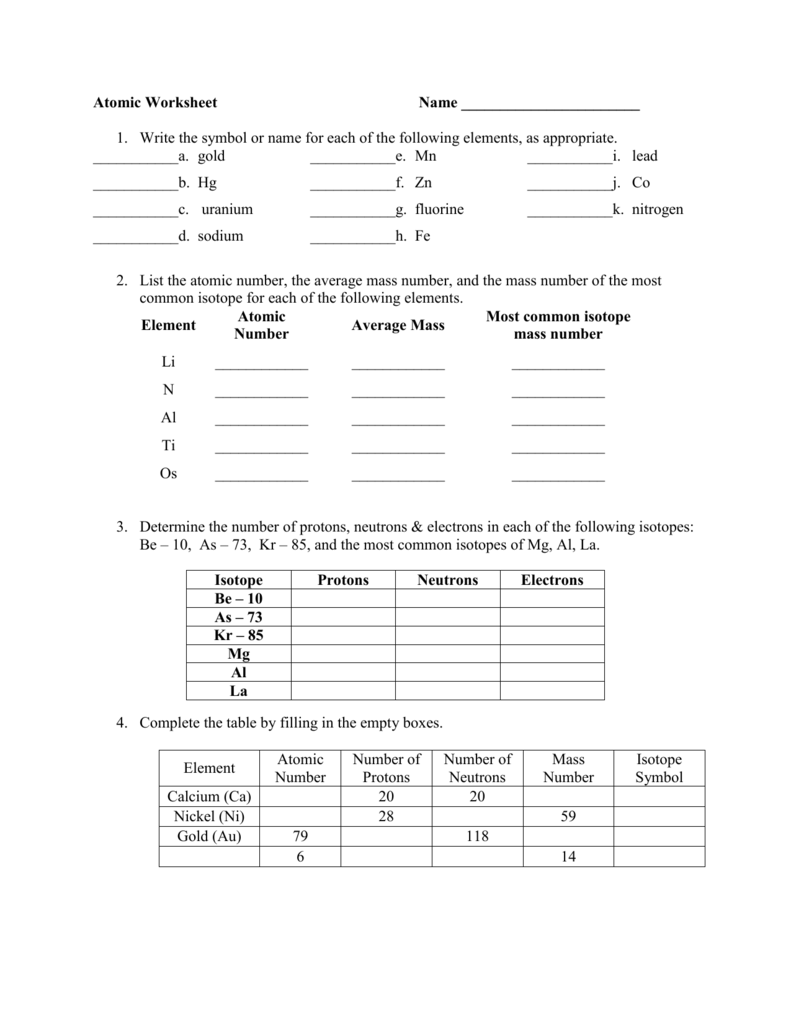
- Atomic Number Nitrogen
- Nitrogen Mass Number 15
- Nitrogen Atomic Symbol
- Nitrogen Mass Number Rounded
- Nitrogen Atomic Weight Of Gas
Element Nitrogen - N
Comprehensive data on the chemical element Nitrogen is provided on this page; including scores of properties, element names in many languages, most known nuclides of Nitrogen. How to free up memory on an android phone. Common chemical compounds are also provided for many elements. In addition technical terms are linked to their definitions and the menu contains links to related articles that are a great aid in one's studies.
Unfortunately, the mass number isn't listed on the Table of Elements. Happily, to find the mass number, all you need to do is round the atomic weight to the nearest whole number. Nitrogen's mass number is 14 since its atomic weight, 14.0067, rounds up to 14. Nitrogen 20 is an isotope of Nitrogen with an atomic weight of 20. The mass number is a.
- The atomic number of nitrogen is 7. What is the mass number of a nitrogen atom with 6 neutrons? An atom has a mass number of 24 and 13 neutrons. What is the atomic number of this atom? 15+ 12-P3+ 15+ 18-P3-12+ 12-Mg. 12+ 10-Mg2+ 12+ 14-Mg2-Charge of K. 1+ Charge of Ba.
- The nitrogen rule states that a molecule that has no or even number of nitrogen atoms has an even nominal mass, whereas a molecule that has an odd number of nitrogen atoms has an odd nominal mass.
Nitrogen Menu
- Nitrogen Page One
- Nitrogen Page Two
- Nitrogen Page Three
Overview of Nitrogen
- Atomic Number: 7
- Group: 15
- Period: 2
- Series: Nonmetals
Nitrogen's Name in Other Languages
- Latin: Nitrogenium
- Czech: Dusík
- Croatian: Dušik
- French: Azote
- German: Stickstoff - r
- Italian: Azoto
- Norwegian: Nitrogen
- Portuguese: Nitrogênio
- Russian: Азот
- Spanish: Nitrógeno
- Swedish: Kväve
Atomic Structure of Nitrogen
- Atomic Radius: 0.75Å
- Atomic Volume: 17.3cm3/mol
- Covalent Radius: 0.75Å
- Cross Section (Thermal Neutron Capture) σa/barns: 1.91
- Crystal Structure: Hexagonal
- Electron Configuration:
- 1s2 2s2p3
- Electrons per Energy Level: 2,5
- Shell Model
- Shell Model
- Ionic Radius: 0.13Å
- Filling Orbital: 2p3
- Number of Electrons (with no charge): 7
- Number of Neutrons (most common/stable nuclide): 7
- Number of Protons: 7
- Oxidation States:±3,5,4,2
- Valence Electrons: 2s2p3
- Electron Dot Model
- Electron Dot Model
Chemical Properties of Nitrogen
- Electrochemical Equivalent: 0.10452g/amp-hr
- Electron Work Function:
- Electronegativity: 3.04 (Pauling); 3.07 (Allrod Rochow)
- Heat of Fusion: 0.3604kJ/mol
- Incompatibilities:
- Ionization Potential
- First: 14.534
- Second: 29.601
- Third: 47.448
- Valence Electron Potential (-eV): 550
Physical Properties of Nitrogen
- Atomic Mass Average: 14.00674
- Boiling Point: 77.5K -195.65°C -320.17°F
- Coefficient of lineal thermal expansion/K-1: N/A
- Conductivity
- Electrical:
Thermal: 0.0002598 W/cmK
- Electrical:
- Density: 1.2506g/L @ 273K & 1atm
- Description:
- Colorless, odorless, tasteless gas
- Enthalpy of Atomization: 472.8 kJ/mole @ 25°C
- Enthalpy of Fusion: 0.36 kJ/mole
- Enthalpy of Vaporization: 2.79 kJ/mole
- Flammablity Class:
- Freezing Point:see melting point
- Heat of Vaporization: 2.7928kJ/mol
- Melting Point: 63.29K -209.86°C -345.75°F
- Molar Volume: 17.3 cm3/mole
- Optical Refractive Index: 1.000298 (gas) 1.197 (liquid)
- Physical State (at 20°C & 1atm): Gas
- Specific Heat: 1.04J/gK

Regulatory / Health
Periodic Table Nitrogen Mass Number
- CAS Number
- 7727-37-9
- OSHAPermissible Exposure Limit (PEL)
- No limits set by OSHA
- OSHA PEL Vacated 1989
- No limits set by OSHA
- NIOSHRecommended Exposure Limit (REL)
- No limits set by NIOSH
- Levels In Humans:
Note: this data represents naturally occuring levels of elements in the typical human, it DOES NOT represent recommended daily allowances.- Blood/mg dm-3: 34300
- Bone/p.p.m: 43000
- Liver/p.p.m: 72000
- Muscle/p.p.m: 72000
- Daily Dietary Intake: n/a
- Total Mass In Avg. 70kg human: 1.8 kg
- Discovery Year: 1772
- Name Origin:
- Greek: zôê (vie).
- Abundance of Nitrogen:
- Earth's Crust/p.p.m.: 25
- Seawater/p.p.m.:
- Atlantic Suface: 0.00008
- Atlantic Deep: 0.27
- Pacific Surface: 0.00008
- Pacific Deep: 0.54
- Atmosphere/p.p.m.: 780900
- Sun (Relative to H=1E12): 8.71E+07
- Sources of Nitrogen:
- Nitrogen can be made by liquification and then fractional distillation of the air. It is very easily done commercially. It can also be made by heating NaN3 to 300 degrees C. Annual world wide production is around 44,000,000 tons.
- Uses of Nitrogen:
- Nitrogen has many industrial uses in the gaseous forms, but probably the most interesting is liquid nitrogen, which is extremely cold. Items that must be frozen to extremely low temperatures for preservation are frequently stored in liquid nitrogen. Fertility clinics store sperm, eggs and embryos used to help infertile couples become pregnant in ampoules in liquid nitrogen.Since nitrogen gas is very stable, at standard temperature and pressure, it is used as the air in inert welding atmospheres. Documents, foods and chemicals are sometimes stored in nitrogen to keep them from oxidizing or reacting with air or water.
- Additional Notes:
Nitrogen in the elemental form was considered to be inert and was even named ozote which refers to the fact that it is not reactive. Of course nitrogen does form compounds, but the gaseous form consists of diamers (2 nitrogens bonded together). The diamer is very stable.
Nitrogen is a major element in organic compounds, especially proteins. Some nitrogen compounds are highly reactive. Trinitrotoluene is TNT or dynamite. Ammonium Nitrate is a fertilizer, but was used as the major explosive ingredient in the Oklahoma City bombing. Anfo, or Ammonium Nitrate and fuel oil mixture is the primary explosive used in the mining industry because it is inexpensive, easy to manufacture and can be easily manufactured near the mine site thus reducing the risks and expenses related to the transportation of explosives. Nitrates, Nitrites and Azides (all nitrogen compounds are either oxidizers or reactives and will react violently under the right conditions.
Nitrogen Menu
- Nitrogen Page One
- Nitrogen Page Two
- Nitrogen Page Three

References
A list of reference sources used to compile the data provided on our periodic table of elements can be found on the main periodic table page.
Related Resources
- Anatomy of the Atom
Answers many questions regarding the structure of atoms. - Molarity, Molality and Normality
Introduces stoichiometry and explains the differences between molarity, molality and normality. - Molar Mass Calculations and Javascript Calculator
Molar mass calculations are explained and there is a JavaScript calculator to aid calculations. - Chemical Database
This database focuses on the most common chemical compounds used in the home and industry.
Citing this page
Atomic Number Nitrogen
If you need to cite this page, you can copy this text:
Kenneth Barbalace. Periodic Table of Elements - Nitrogen - N. EnvironmentalChemistry.com. 1995 - 2021. Accessed on-line: 4/24/2021
https://EnvironmentalChemistry.com/yogi/periodic/N.html/
.

Linking to this page
Nitrogen Mass Number 15
If you would like to link to this page from your website, blog, etc., copy and paste this link code (in red) and modify it to suit your needs:
echo Periodic Table of Elements: Nitrogen - N (EnvironmentalChemistry.com)- Comprehensive information for the element Nitrogen - N is provided by this page including scores of properties, element names in many languages, most known nuclides and technical terms are linked to their definitions.
.
Nitrogen Atomic Symbol
NOTICE: While linking to articles is encouraged, OUR ARTICLES MAY NOT BE COPIED TO OR REPUBLISHED ON ANOTHER WEBSITE UNDER ANY CIRCUMSTANCES.
PLEASE, if you like an article we published simply link to it on our website do not republish it. Dropbox installer mac not working.
Molar Mass, Molecular Weight and Elemental Composition Calculator
Molar mass of nitrogen is 28.01340 ± 0.00040 g/mol Compound name is nitrogen Convert between N2 weight and moles
Elemental composition of N2
Sample reactions for N2
Formula in Hill system is N2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Computing molar mass (molar weight)To calculate molar mass of a chemical compound enter its formula and click 'Compute'. In chemical formula you may use:
Molar mass calculator also displays common compound name, Hill formula, elemental composition, mass percent composition, atomic percent compositions and allows to convert from weight to number of moles and vice versa. Computing molecular weight (molecular mass)To calculate molecular weight of a chemical compound enter it's formula, specify its isotope mass number after each element in square brackets.Examples of molecular weight computations: C[14]O[16]2, S[34]O[16]2. Definitions of molecular mass, molecular weight, molar mass and molar weight
Give us feedback about your experience with Molecular Weight Calculator. Related: Molecular weights of amino acids | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| molecular weights calculated today |
| Back to Online Chemical Tools Menu |

Regulatory / Health
Periodic Table Nitrogen Mass Number
- CAS Number
- 7727-37-9
- OSHAPermissible Exposure Limit (PEL)
- No limits set by OSHA
- OSHA PEL Vacated 1989
- No limits set by OSHA
- NIOSHRecommended Exposure Limit (REL)
- No limits set by NIOSH
- Levels In Humans:
Note: this data represents naturally occuring levels of elements in the typical human, it DOES NOT represent recommended daily allowances.- Blood/mg dm-3: 34300
- Bone/p.p.m: 43000
- Liver/p.p.m: 72000
- Muscle/p.p.m: 72000
- Daily Dietary Intake: n/a
- Total Mass In Avg. 70kg human: 1.8 kg
- Discovery Year: 1772
- Name Origin:
- Greek: zôê (vie).
- Abundance of Nitrogen:
- Earth's Crust/p.p.m.: 25
- Seawater/p.p.m.:
- Atlantic Suface: 0.00008
- Atlantic Deep: 0.27
- Pacific Surface: 0.00008
- Pacific Deep: 0.54
- Atmosphere/p.p.m.: 780900
- Sun (Relative to H=1E12): 8.71E+07
- Sources of Nitrogen:
- Nitrogen can be made by liquification and then fractional distillation of the air. It is very easily done commercially. It can also be made by heating NaN3 to 300 degrees C. Annual world wide production is around 44,000,000 tons.
- Uses of Nitrogen:
- Nitrogen has many industrial uses in the gaseous forms, but probably the most interesting is liquid nitrogen, which is extremely cold. Items that must be frozen to extremely low temperatures for preservation are frequently stored in liquid nitrogen. Fertility clinics store sperm, eggs and embryos used to help infertile couples become pregnant in ampoules in liquid nitrogen.Since nitrogen gas is very stable, at standard temperature and pressure, it is used as the air in inert welding atmospheres. Documents, foods and chemicals are sometimes stored in nitrogen to keep them from oxidizing or reacting with air or water.
- Additional Notes:
Nitrogen in the elemental form was considered to be inert and was even named ozote which refers to the fact that it is not reactive. Of course nitrogen does form compounds, but the gaseous form consists of diamers (2 nitrogens bonded together). The diamer is very stable.
Nitrogen is a major element in organic compounds, especially proteins. Some nitrogen compounds are highly reactive. Trinitrotoluene is TNT or dynamite. Ammonium Nitrate is a fertilizer, but was used as the major explosive ingredient in the Oklahoma City bombing. Anfo, or Ammonium Nitrate and fuel oil mixture is the primary explosive used in the mining industry because it is inexpensive, easy to manufacture and can be easily manufactured near the mine site thus reducing the risks and expenses related to the transportation of explosives. Nitrates, Nitrites and Azides (all nitrogen compounds are either oxidizers or reactives and will react violently under the right conditions.
Nitrogen Menu
- Nitrogen Page One
- Nitrogen Page Two
- Nitrogen Page Three
References
A list of reference sources used to compile the data provided on our periodic table of elements can be found on the main periodic table page.
Related Resources
- Anatomy of the Atom
Answers many questions regarding the structure of atoms. - Molarity, Molality and Normality
Introduces stoichiometry and explains the differences between molarity, molality and normality. - Molar Mass Calculations and Javascript Calculator
Molar mass calculations are explained and there is a JavaScript calculator to aid calculations. - Chemical Database
This database focuses on the most common chemical compounds used in the home and industry.
Citing this page
Atomic Number Nitrogen
If you need to cite this page, you can copy this text:
Kenneth Barbalace. Periodic Table of Elements - Nitrogen - N. EnvironmentalChemistry.com. 1995 - 2021. Accessed on-line: 4/24/2021
https://EnvironmentalChemistry.com/yogi/periodic/N.html/
.
Linking to this page
Nitrogen Mass Number 15
If you would like to link to this page from your website, blog, etc., copy and paste this link code (in red) and modify it to suit your needs:
echo Periodic Table of Elements: Nitrogen - N (EnvironmentalChemistry.com)- Comprehensive information for the element Nitrogen - N is provided by this page including scores of properties, element names in many languages, most known nuclides and technical terms are linked to their definitions.
.
Nitrogen Atomic Symbol
NOTICE: While linking to articles is encouraged, OUR ARTICLES MAY NOT BE COPIED TO OR REPUBLISHED ON ANOTHER WEBSITE UNDER ANY CIRCUMSTANCES.
PLEASE, if you like an article we published simply link to it on our website do not republish it. Dropbox installer mac not working.
Molar Mass, Molecular Weight and Elemental Composition Calculator
Molar mass of nitrogen is 28.01340 ± 0.00040 g/mol Compound name is nitrogen Convert between N2 weight and moles
Elemental composition of N2
Sample reactions for N2
Formula in Hill system is N2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Computing molar mass (molar weight)To calculate molar mass of a chemical compound enter its formula and click 'Compute'. In chemical formula you may use:
Molar mass calculator also displays common compound name, Hill formula, elemental composition, mass percent composition, atomic percent compositions and allows to convert from weight to number of moles and vice versa. Computing molecular weight (molecular mass)To calculate molecular weight of a chemical compound enter it's formula, specify its isotope mass number after each element in square brackets.Examples of molecular weight computations: C[14]O[16]2, S[34]O[16]2. Definitions of molecular mass, molecular weight, molar mass and molar weight
Give us feedback about your experience with Molecular Weight Calculator. Related: Molecular weights of amino acids | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| molecular weights calculated today |
| Back to Online Chemical Tools Menu |
Nitrogen Mass Number Rounded
© 2021 webqc.org All rights reserved
Nitrogen Atomic Weight Of Gas
| Periodic table |
| Unit converters |
| Chemistry tools |
| Chemical Forum |
| Chemistry FAQ |
| Constants |
| Symmetry |
| Chemistry links |
| Link to us |
| Contact us |
How to cite? |
WebQC.Org online education free homework help chemistry problems questions and answers |

